Insomnia
Home // Insomnia
What is Insomnia?
Insomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing poor sleep quality. People with insomnia often struggle to initiate or maintain a regular sleep pattern, leading to persistent feelings of tiredness and impaired daytime functioning. It can be a temporary or chronic condition and may be caused by various factors, such as stress, anxiety, depression, certain medications, or lifestyle habits. Insomnia can have significant impacts on a person’s physical health, mental well-being, and overall quality of life. Treatment approaches for insomnia include improving sleep hygiene, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and in some cases, medication under the guidance of a healthcare professional.

Reasons Behind Insomnia
- Stress and Anxiety: High levels of stress or excessive worrying can make it difficult to fall asleep or maintain a restful sleep throughout the night.
- Poor Sleep Habits: Irregular sleep schedules, inconsistent bedtime routines, excessive napping during the day, or engaging in stimulating activities before bed can disrupt sleep patterns.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions such as chronic pain, respiratory problems, gastrointestinal issues, hormonal imbalances, or neurological disorders can interfere with sleep.
- Medications: Some medications, including certain antidepressants, stimulants, and corticosteroids, can affect sleep quality and contribute to insomnia.
- Substance Abuse: The consumption of substances like caffeine, nicotine, alcohol, or certain drugs can disrupt sleep patterns and lead to insomnia.
- Environmental Factors: Uncomfortable sleeping conditions, such as excessive noise, an uncomfortable bed, bright lights, or extreme temperatures, can make it difficult to fall or stay asleep.
- Sleep Disorders: Conditions like sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome (RLS), or narcolepsy can disrupt sleep and contribute to insomnia.
Common Symptoms of Insomnia
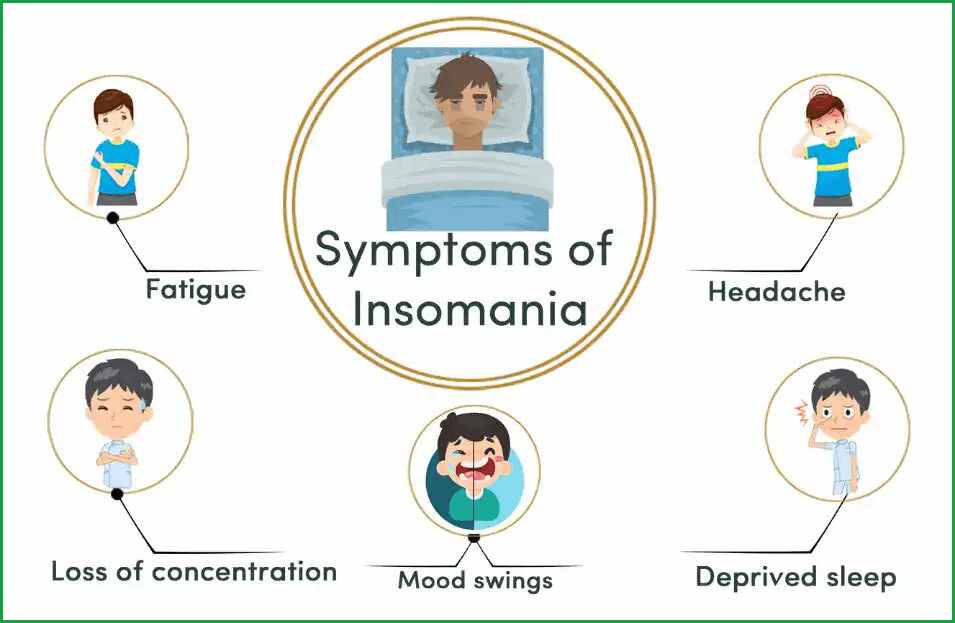
- Difficulty falling asleep at night
- Waking up frequently during the night
- Trouble returning to sleep after waking up in the middle of the night
- Waking up too early in the morning
- Feeling tired and fatigued upon waking
- Daytime sleepiness and lack of energy
- Difficulty concentrating, focusing, or remembering things
- Irritability, mood swings, or increased anxiety
- Increased errors or accidents due to lack of alertness
- Dependence on sleep aids or medications to fall asleep
Effective Treatments for Insomnia
Insomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing poor sleep quality. There are several short-term and long-term treatments available to manage insomnia. Here are some commonly used methods:
- Sleep hygiene: Practicing good sleep habits such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, avoiding stimulating activities before bedtime, and limiting caffeine and alcohol intake.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I): A structured therapeutic approach that addresses the underlying thoughts, beliefs, and behaviors contributing to insomnia. CBT-I helps individuals develop healthy sleep habits and techniques to manage anxiety or racing thoughts at night.
- Medications: In some cases, doctors may prescribe sleep medications for short-term relief. These medications include over-the-counter sleep aids, sedatives, or prescribed medications like benzodiazepines or non-benzodiazepine hypnotics. However, these medications should be used under medical supervision due to potential side effects and dependency risks.
- Relaxation techniques: Practices such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, meditation, or mindfulness can help calm the mind and prepare the body for sleep.
- Light therapy: Exposure to bright light, particularly in the morning, can help regulate the body’s internal clock and improve sleep-wake patterns, especially for individuals with circadian rhythm disorders.
- Avoid napping: Limiting daytime napping, especially close to bedtime, can help build up sleep pressure and improve the ability to fall asleep at night.
- Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, ideally earlier in the day, can promote better sleep. However, vigorous exercise close to bedtime may have a stimulating effect, so it’s best to schedule exercise sessions earlier in the day.
It’s important to consult a healthcare professional to discuss your specific symptoms and determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your insomnia.
